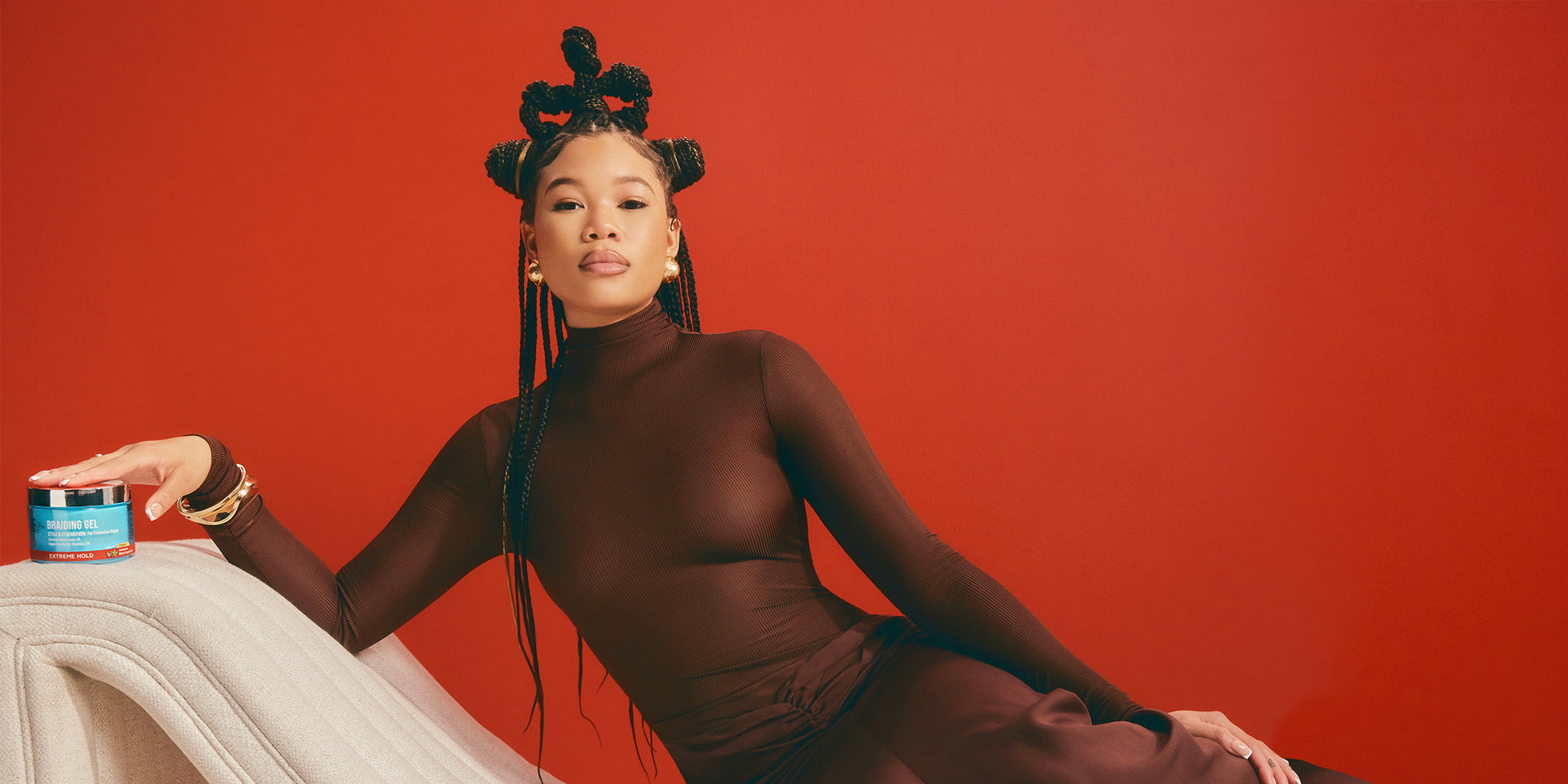
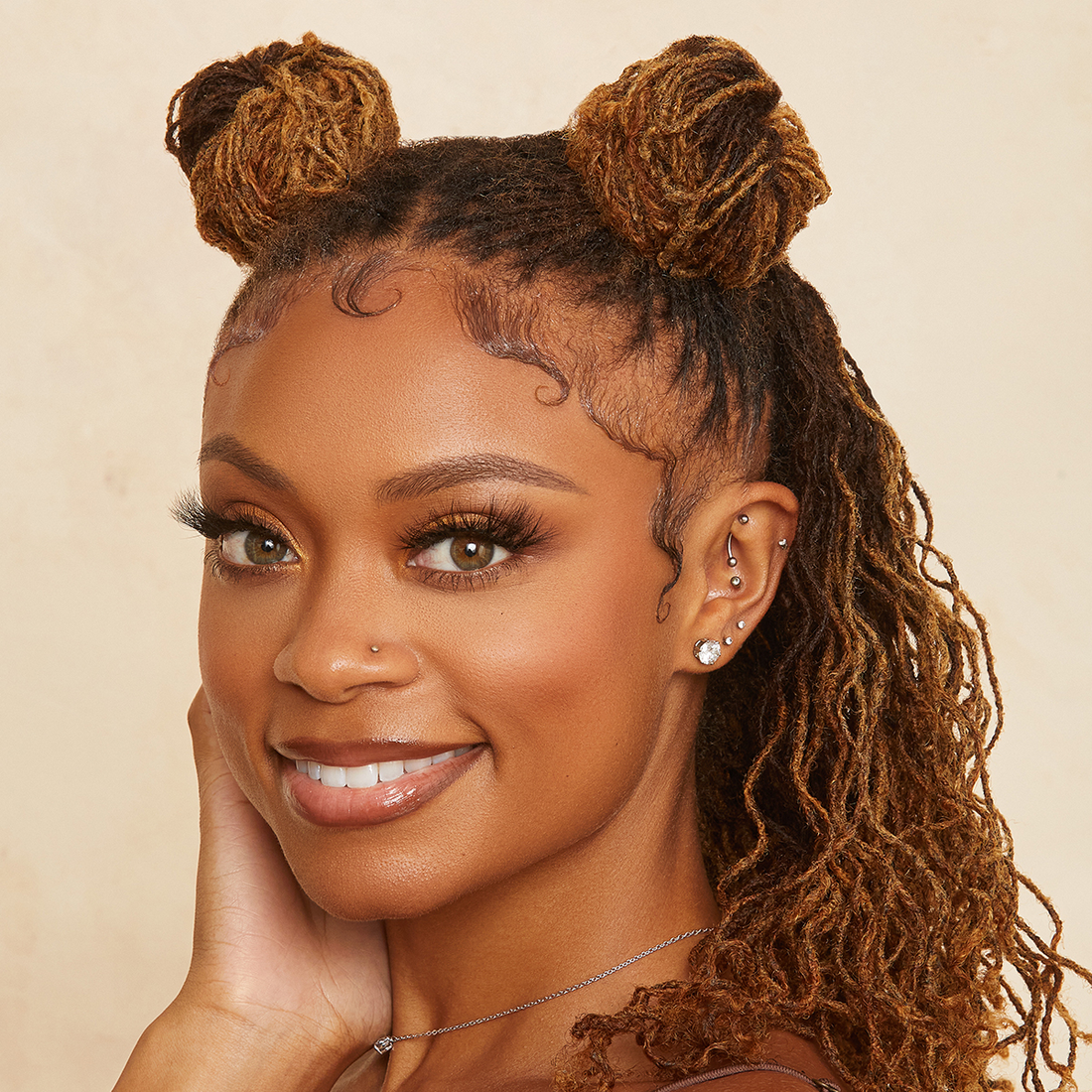
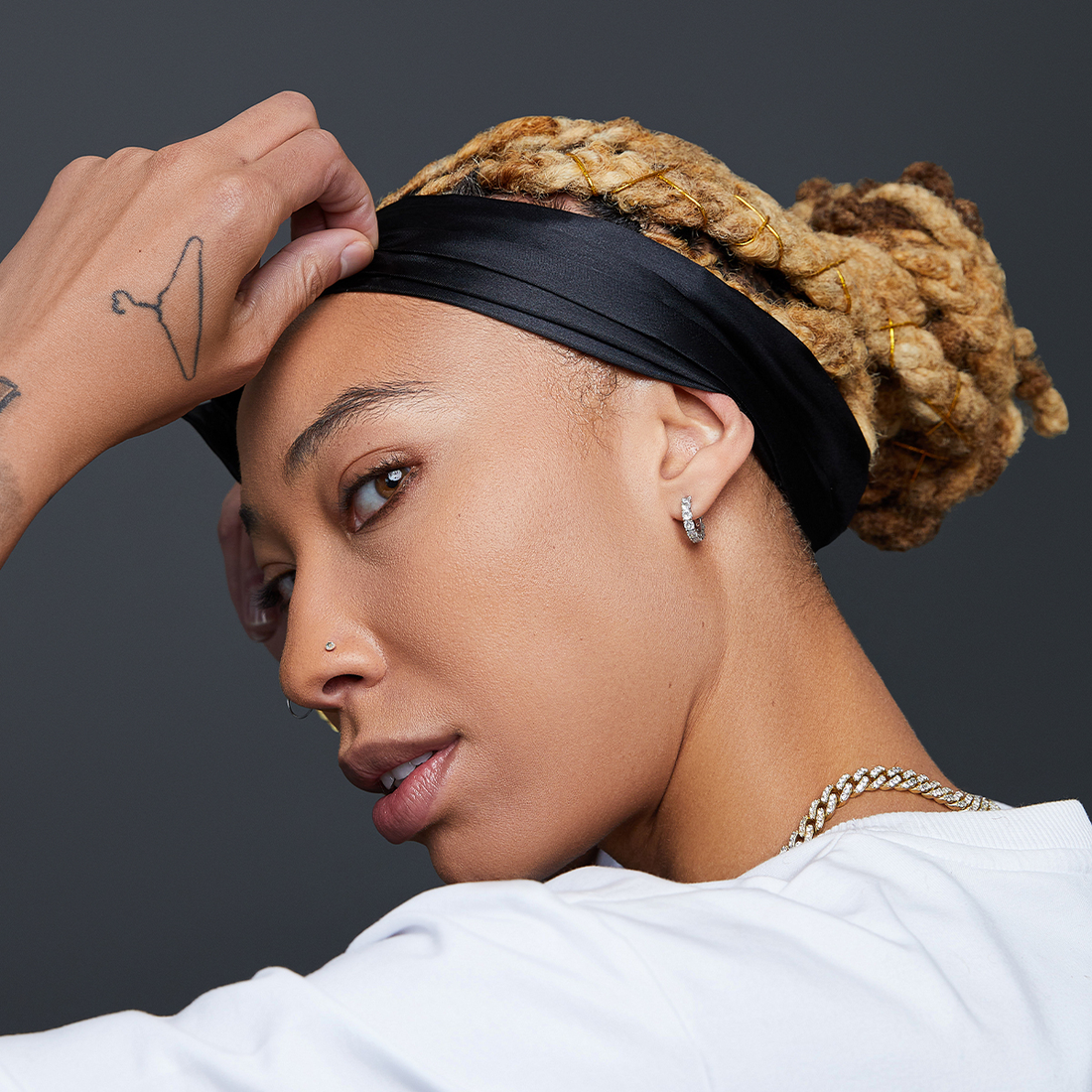
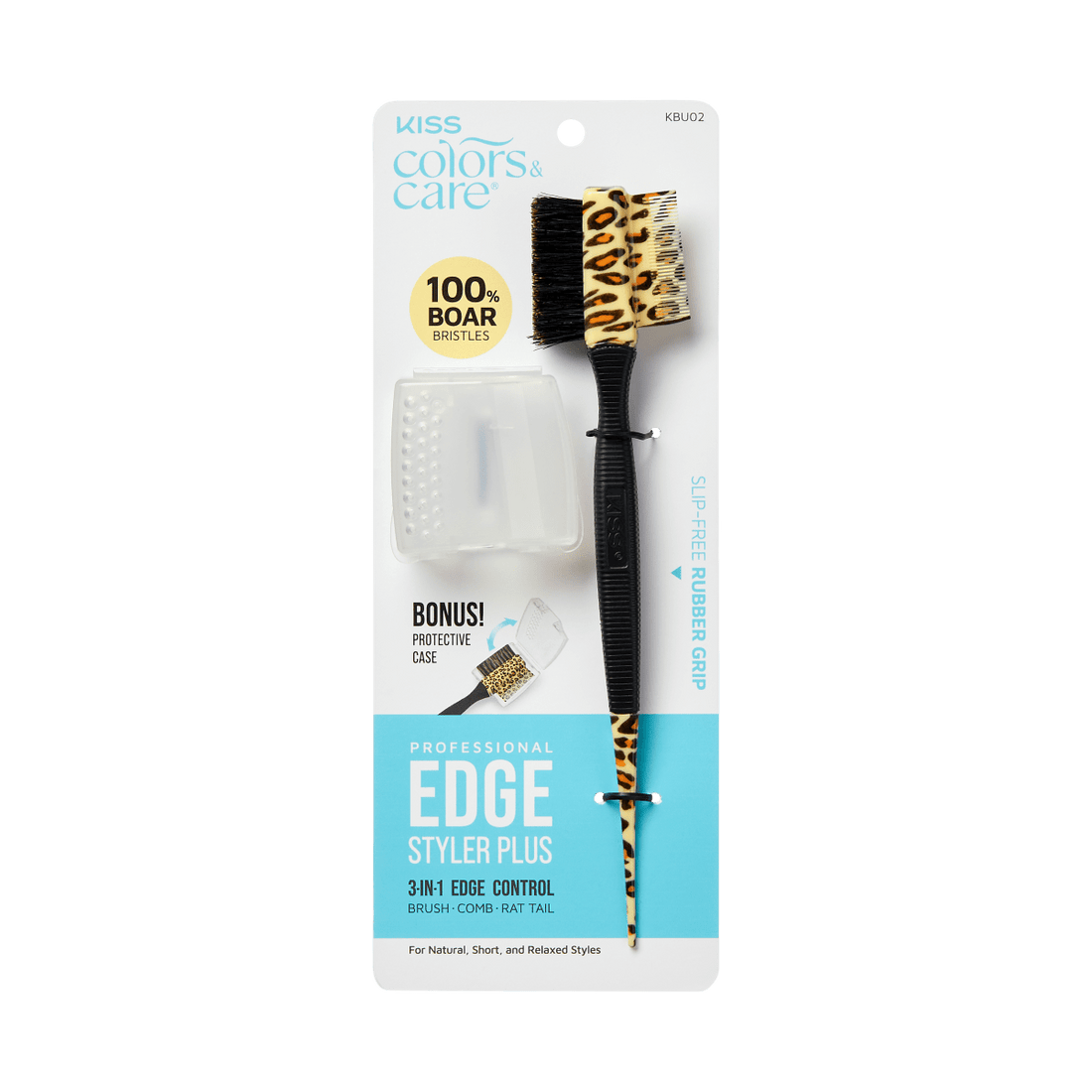
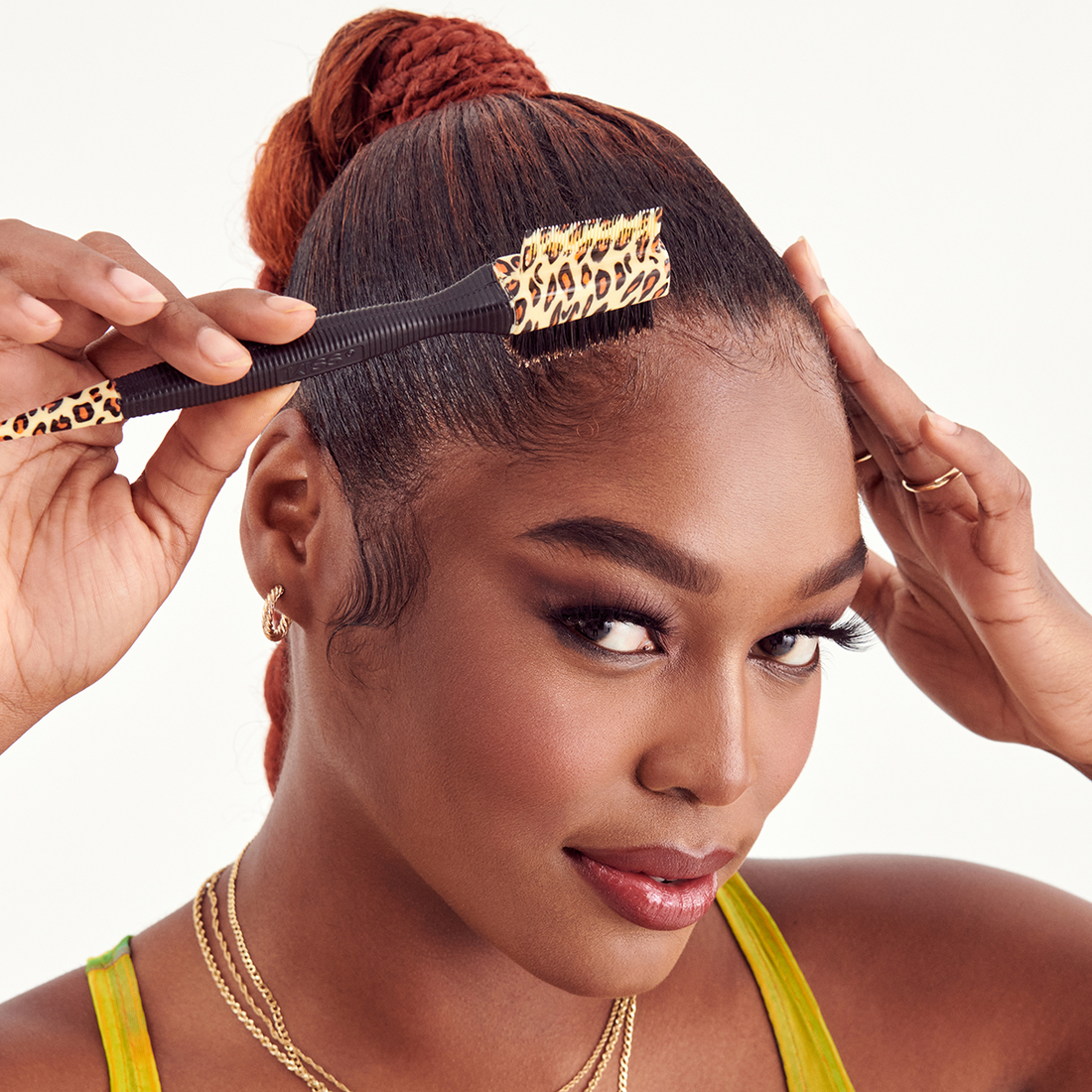
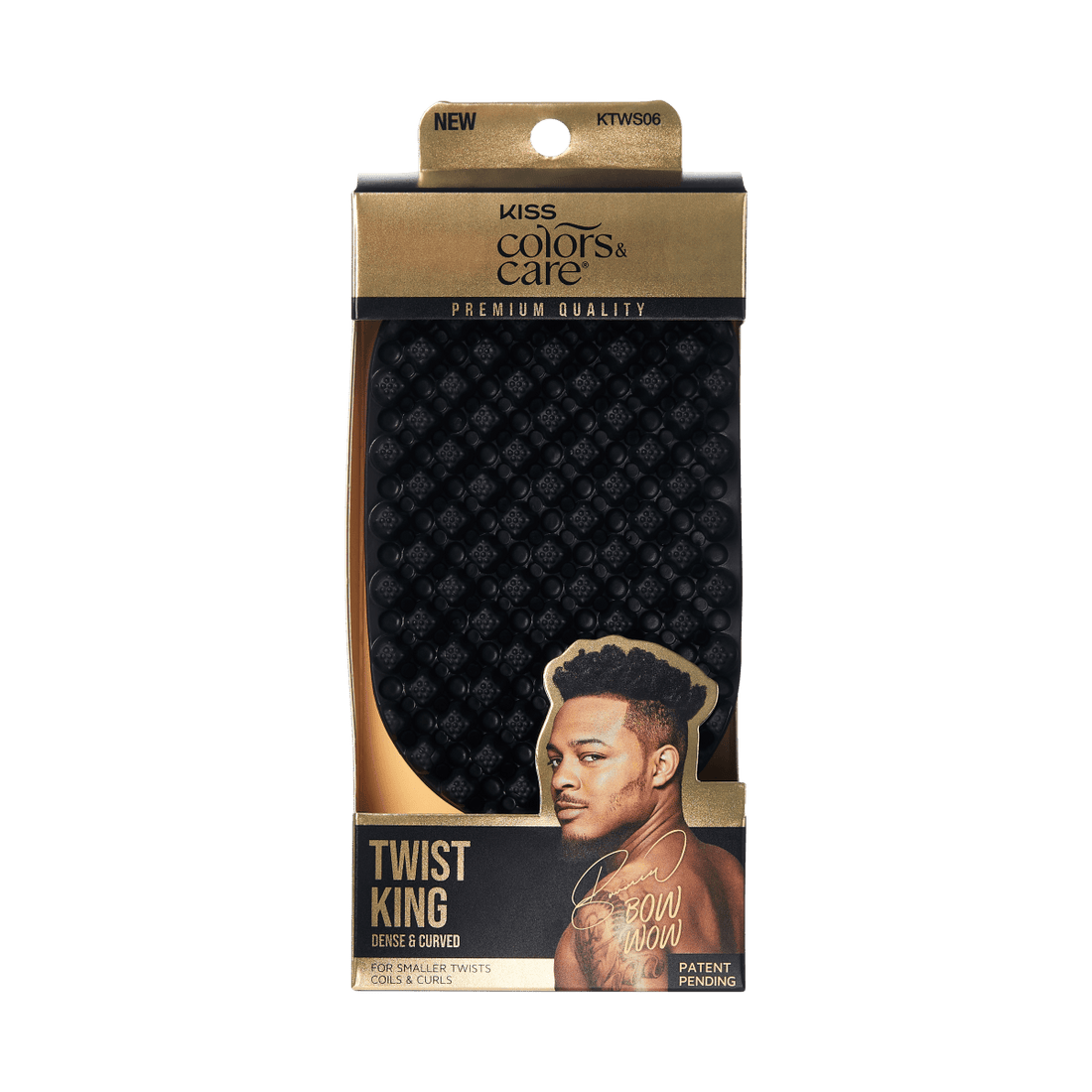
BEST SELLERS
GET THE LATEST TIPS FROM OUR IN-HOUSE PRO
Tap in to learn from celebrity stylist Janel Sealy Smith

Boho Bantu Knots

DIY Sleek Pony

Box Braids Made Easy
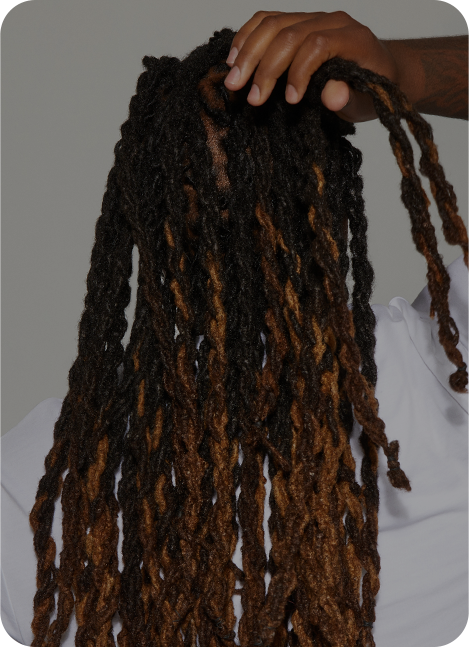

Loc Retwist
OUR PROMISE
We’re dedicated to bringing you the hottest trends at the highest quality so you can nourish, protect and show off your style with confidence.
SHARE YOUR STYLE WITH US
#kisscolorsandcare #colorsandcare #kisshair